Trading technical indicators with binary options can be a highly profitable trading style if you know how to do it right. This article explains the basics and three example strategies you can use. Here’s what you learn in detail:
- What are technical indicators?
- Why are technical indicators and digital options a great combination?
- Three examples of technical indicator strategies
This information will allow you to trade binary options along with technical options instantly.
What is an indicator?
Technical indicators are useful trading tools for price action traders to understand what is happening in the market and make predictions about what will happen next.
Some indicators bring their results directly onto price charts, allowing analysts to easily compare them to current market prices. Other indicators display results using a separate window. The best known example of this type of indicator is the oscillator. This indicator produces a value that oscillates between 0 and 100. This value and its changes over time allow us to understand what happened in the past and what will happen next.
There are thousands of indicators, but these are the most important types and a few examples.
- Support and Resistance: This indicator predicts support and resistance levels as the market turns around. A breakout of these levels will move you away from the price level. Example: Bottom, Fibonacci Retracement, Pivot Point (PP), Top.
- Trend: This indicator helps you assess the strength and reliability of a trend. Examples: Average Direction Index (ADX), Commodity Channel Index (CCI), Downtrend Oscillator (DPO), Sure Oscillator (KST), Ichimoku Kinkohyo, Moving Average Convergence/Dispersion (MACD), Mass Exponential Moving Average (MA), Parabolic SAR (SAR), Smart Money Index (SMI), Trix Vortex Indicator (VI).
- Momentum: This metric helps you understand the momentum of your workout. Examples: MFI (Money Flow Index), RSI (Relative Strength Index), Stochastic Oscillator, TSI (True Strength Index), Ultimate Oscillator Williams % R (% R).
- Volume: This indicator uses volume (the number of assets sold or bought) to assess whether an investor is more bullish or bearish. Examples: Accumulation/Distribution Line, Ease of Movement (EMV), Force Index (FI), Volume Index (NVI), On Balance Volume (OBV), Put/Call Ratio (PCR), Volume Price Trend (VPT).</li >
- Volatility Indicator: This indicator measures the strength of a movement, helping traders to make different predictions, especially for binary option types that use target prices, such as One Touch Options, Boundary Options, or Ladder Options. give. Examples: Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger Bands (BB), Donchian Channel, Keltner Channel, CBOE, Market Volatility Index (VIX), Standard Deviation (σ).
You don’t have to learn all of these indicators. Go through each category, choose the one you like the most, and get it from there. It’s best to start with metrics that you truly understand and like. You can add more indicators to your strategy later so your trades can evolve naturally.
Why are indicators good for binary options?
Most binary options traders rely heavily on technical indicators. There are mainly three reasons for this strong link between binary options and technical indicators.
- Technical indicators simplify price action analysis. Price action is the only way to predict what’s going to happen on a short time frame like we use within binary options. However, just looking at price movements can be confusing. Technical Indicators can filter out the most important information on a price chart and display it in a way that everyone can instantly understand. This simplification makes trading faster and easier.
- Indicators protect transactions. Analyzing the market without help requires a lot of information. Complexity leads to mistakes and bad decisions, which is costly. Technical indicators help you make more money in a simpler way by eliminating these mistakes.
- Indicators can show traders what they can’t do. Technical indicators analyze hundreds of data sets in seconds, filter out the most relevant information and display it in a way everyone can understand. Much of this information is inaccessible without the help of technical indicators. Calculating the Bollinger Bands for 50 assets with 10 time periods each would take years. Technical analysis adds a layer of information to your trading that was previously hidden in it.
These points are why technical indicators and binary options are such a great combination.
What are the leading indicators?
A leading indicator is a special form of market indicator. A market indicator is anything that helps you understand if an asset’s price will rise or fall in the future. They provide important, useful, and easy-to-interpret tools for binary options traders. With the right strategy, you can anticipate new market movements and find the ideal time to invest.
These indicators can be classified into two types.
- Leading indicators. This type of indicator predicts what will happen to the price of an asset.
- Lag indicator. This type of indicator tells you what has happened to the price of an asset. This information helps predict what might happen next, but the indication itself focuses on the past. This is a huge difference between the two types of metrics.
The goal of leading indicators is to tell users where the price of an asset is headed. A good example of a leading indicator in another sector is the Business Climate Index. Business managers report their expectations for the future, and the index creates an aggregated value that can be easily compared to previous months and years. Values and changes over time help predict whether the economy will improve or deteriorate.
The same goes for key financial indicators. They measure something and the resulting value tells you if things are going to get better.
Why use leading indicators?
Leading indicators serve a very important purpose. It helps you understand if an existing movement will continue sooner or end soon. This sign helps you find great trading opportunities and avoid bad trading opportunities.
For example, let’s say you’re moving upwards.
- When your leading indicators say the move will continue, you know this is an appropriate time to trade high options.
- If your leading indicators say the move is about to end, you know that now is not the right time to trade high options . You should trade options that predict an exit from the market or an imminent end of movement.
For trend followers, swing traders, and just about everyone else, key indicators add vital information to your trading style. They can filter out bad signals, find new trading opportunities and win more trades.
Popular Examples of Key Indicators
There are hundreds of key indicators. Some of them are similar and very different. To help you understand leading indicators better, let’s now take a look at three leading indicators that can give you a good feel for different types of leading indicators.
Example 1: Money Flow Index (MFI)
The Money Flow Index (MFI) is such a popular leading indicator because it helps traders quickly assess the strength of a trend.
As the name suggests, an MFI compares the money flowing into an asset with the money going out. To do this, the average of the high, low, and close prices for each period is multiplied by the period’s volume, then the sum of all periods in which the price has risen is divided by the sum of all periods in which the price has declined.
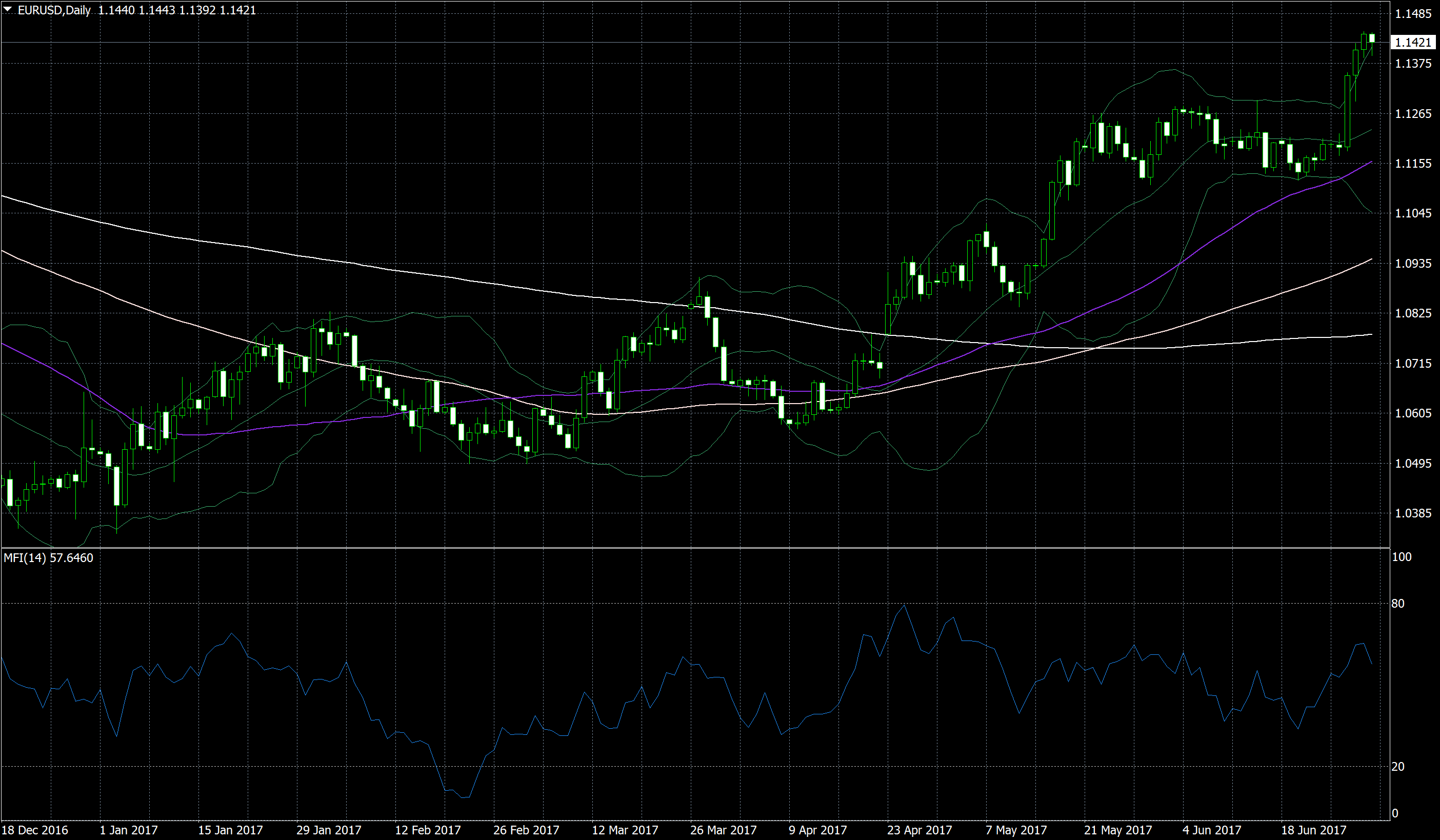
The result is a value between 0 and 100.
- When the MFI reads 100, all the money has flowed into the asset, and every period has an uptrend.
- If the MFI reads 0, all the money has flowed out of the asset and the price has fallen in all periods.
- When the MFI reads 50, the number of assets sold and bought is exactly the same.
All values above 50 indicate that more people sold the asset than bought it, all values below 50 indicate the opposite.
The number of MFIs and their changes over time allow two predictions about future market movements.
- extreme value. If the MFI is too high (usually above 70) or too low (usually less than 30), the market enters an extreme region. Traders assume that such extreme values mean that too many traders have already bought and sold assets and that there are no more traders left who can buy and sell assets and move on. As a result, they predict that the movement is in trouble and will soon turn around or go through consolidation before moving on. Some traders use this signal to stop investing in a movement. Some are already investing in the opposite direction.
- Convergence / divergence. When the market forms new extremes in a trend (either new highs in an uptrend or new lows in a downtrend), the MFI should reflect these moves and create new extremes. When the MFI doesn’t reflect the market’s new highs/lows with its own highs/lows, traders are starting to push the trend. While this was still enough to create new extremes, the trade would end if momentum continued to decline. Some traders use this signal to stop investing in the trend, while some trade in the opposite direction.
Of course, you can also interpret MFI in the opposite way.
- When the MFI reads between 30 and 70, there is plenty of room for the market to continue its current move. Most traders will predict that the move will last for a while and invest accordingly.
- If the MFI mirrors the current trend, the trend will stay the same. Most traders will predict that the trend will continue and invest accordingly.
MFI is a key indicator because it predicts that a trend or movement will continue or end soon. A lag indicator informs you about past movements.
Since the value of MFI oscillates between 0 and 100, it is called an oscillator. Most other oscillators are also leading indicators. If you want a simple idea to guide your investment decisions, take a look at the other oscillators Technical Analysis has to offer.
Example 2: Commodity Channel Index (CCI)
The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) works with all types of assets, not just commodities.
Simply put, CCI calculates how far an asset is from the statistical mean. The theory is that if an asset strays too far from its average price, it should return soon. CFI, like MFIs, assumes that too many traders are buying and selling assets and there is no one to force the market in this direction. We need to turn around and strengthen it.
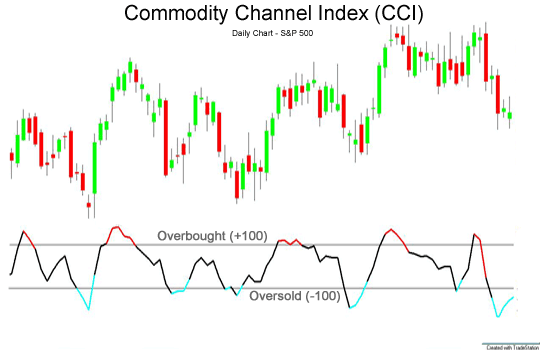
Specifically, the CCI relates the result to a smoothed moving average by multiplying the average high, low, and close prices of the last completed period by 0.015.
- A value above 100 indicates that the asset is trading above 1.015 times its moving average value.
- A value below -100 indicates that the asset is trading below 0.985 times its moving average value.
In either case, the CCI predicts that the market has moved too far from the moving average and that the move is about to return.
Some traders wait before investing.
- If CCI rises above 100, wait until it starts to fall.
- Wait until the CCI falls below -100 to start investing.
These traders use CCI more as a lagging indicator. To use the CCI as a leading indicator, you should invest when the market crosses the +100/-100 line. Then invest in projections. Invest in reaction when trading in a changing direction and use the CCI as a lagging indicator.
Sometimes the line between lagging and leading indicators can be thin. As long as you know the difference and trade accordingly, that’s fine.
Example 3: Relative Strength Index (RSI)
At first glance, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) appears to be very similar to the Money Flow Index (MFI). Both are oscillators and produce values between 0 and 100 and have overbought and oversold zones.
The difference between the two indicators is that RSI only focuses on price movements, while MFI also takes into account the volume in each period. The RSI treats all periods the same, but the MFI gives more weight to periods of high volume and less weight to periods of low volume.
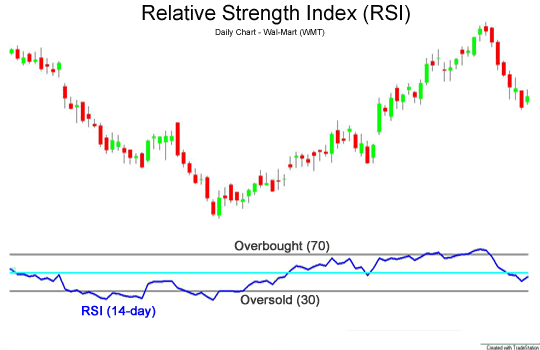
Other than that, you can use RSI just like MFI. When R90 is between 30 and 70, your current move should still have a margin. Trends are good when they reflect trends.
MFI or RSI are not always better. Which indicator you should use depends on your strategy, personality and beliefs about the market.
- Some traders argue that volume should be ignored as it trades price, not volume. They also say that in the short time frames of binary options, the volumes are too similar to be effective. These traders should use the RSI.
- Some traders claim that volume has a big impact because it points in the direction of supporting more traders. These traders must use MFI.
How to Trade Key Indicators in Binary
All key indicators can be the sole foundation of your trading strategy or filter signals as an add-on to your current strategy. We will present a strategy using key indicators in two ways.
Strategy 1: Trade MFI quarters with high or low options
We have already pointed out that MFI reflects intact trends.
- When a intact uptrend makes a new peak, so does the MFI.
- When the intact downtrend makes a new low, the MFI also makes a new low.
If the MFI doesn’t reflect the new extremes of a trend, there’s something wrong with the trend. The trend is losing momentum, and it still has enough strength to create new extremes, but this seems to be the last extreme of the trend.
The high/low option provides the perfect tool to trade this prediction.
- Invest in lower options when MFI diverges into an uptrend.
- Invest in options higher when the MFI turns into a downtrend.
An important part of this strategy is obtaining expiry rights. It is very likely that the market will follow the MFI divergence by changing direction or moving sideways, but these moves take time to develop. It is important to choose a period long enough to give the market this time.
For example, if you find an MFI divergence on a 5-minute chart, a 15-minute expiration is not sufficient. The market takes at least 10 periods to come back and a 15 minute expiry is worth 3 bars. Choosing an hour expiry increases your chances of winning the trade.
You can also trade this strategy for the RSI. Just toggle the indicator without changing anything else.
You can also replace high/low options with lower-risk ladder options. Ladder options work the same as high/low options, but allow you to use a price other than the current market price as a reference point for your predictions.
- If an MFI divergence occurred in an uptrend, you would expect the market to trade below the current market price and above it.
- If the MFI divergence occurred in a downtrend, you would expect the market to trade above the current market price below it.
This is a safer version of the strategy. Instead of using the current market price as a reference point for forecasting, we use a higher price in the direction the market is expected to move away. This strategy not only gets you a higher percentage on your trades, but also lower payouts. Decide for yourself which strategy you want to use.
Strategy 2: Trend Filtering via RSI
Trend following strategies follow a simple principle.
- Invest in rising prices in an uptrend.
- In a downtrend, invest in falling prices.
Despite this simplicity, many traders are afraid to invest in a trend that is about to end. These traders can use RSI to filter signals.
- If the RSI reflects a trend, invest in the trend.
- If the RSI is out of trend, don’t invest in the trend.
Adding the RSI to a trend-following strategy allows traders to win more trades and make more money with simple confirmations.
Do not change the rest of the strategy. Use the same maturity as before and invest the same percentage of your total account balance per trade.
Strategy 3: Trade extreme areas with high or low MFI options
In addition to variance, MFI also produces predictions when movement enters extreme areas. This prediction enables a simple trading strategy.
- Invest in lower options when MFI enters overbought territory.
- Invest in lower options when the MFI enters oversold territory.
The success of this strategy depends on your ability to choose the right expiry. You should avoid choosing expirations that are too short because the market needs time to turn around. On the other hand, if you choose too long to expiry, you may end up moving by the time the option expires.
Experience will help you find the right maturity. The perfect setup depends on your situation, chart time period and asset characteristics. To find a rough number to start with, try about 5 cycles and then take it from there.
Like the first strategy, you can also trade this strategy based on RSI or low-risk ladder options.
Leading Indicators – Summary
Leading indicators are important, useful, and easy-to-interpret market analysis tools. Binary options traders can use leading indicators as the sole basis for their strategies or to filter signals. It is especially helpful for finding the right timing and avoiding bad trading opportunities.
What is a Lag Indicator?
Lag indicators are an important aspect of any market analysis strategy. This article will explain everything you need to know to trade binary options based on the lag indicator. Also understand the advantages, disadvantages and ideal areas of use.
The difference between leading and lagging trade indicators is the same.
- The Lag Trade Indicator tells you what happened to an asset’s price in the past in a way that helps you predict what might happen next.
- Key indicators predict how different factors will affect an asset’s price.
This difference is why lagging indicators are especially useful during trend periods. When the market is trending, lagging indicators can help you make great predictions. However, many laggard indicators use predictive quality when the market is not trending.
Lag indicators serve an important purpose and are an important part of any market analysis strategy. Let’s take a closer look at three examples of popular lagging indicators to learn how to use them for trading.
Popular Examples of Lag Indicators
There are hundreds of lag indicators out there, but let’s keep it simple. Here are the three most popular indicators that every trader should know about.
Example 1: Trend
The most popular example of a lagging indicator is the trend. A trend is a zig-zag movement that propels the market to new highs and lows.
Trends are zig-zag movements because markets never move in a straight line. Every once in a while, every workout needs a break to build up new momentum. It is impossible for all traders to continue buying continuously.
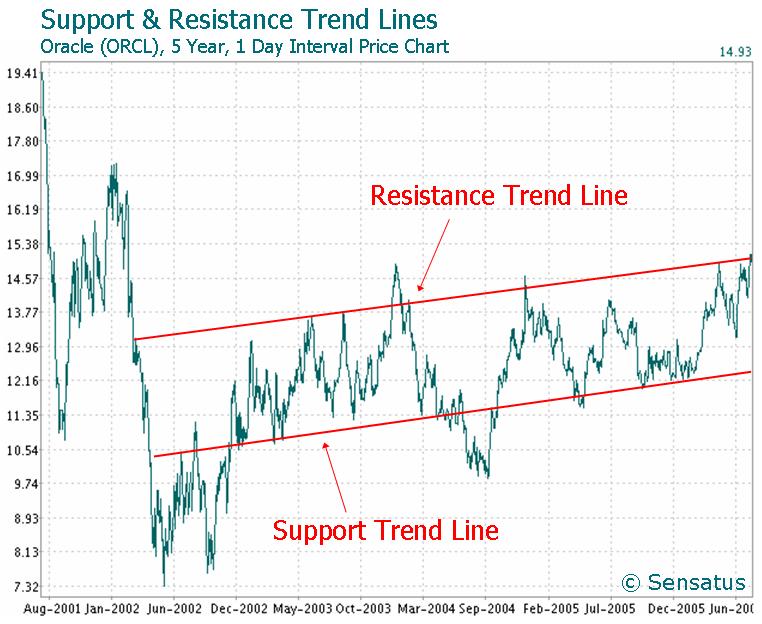
That’s why the trend moves two steps forward and one step back. The resulting zig-zag movement is easy to identify and allows for accurate predictions.
- An uptrend creates consistently higher highs and lows.
- Downtrends consistently make lower lows and higher highs.
A trend strategy predicts that the current trend will continue.
- When the market is in an uptrend, trend traders invest in rising prices.
- When the market is in a downtrend, trend traders invest in falling prices.
Some traders trade every swing in the trend. A swing is a movement from highs to lows, and by trading multiple swings during a trend, swing traders hope to increase their profits.
Of course, no trend will continue indefinitely. However, no matter how high or low the option is, you only need to win 60% of your trades to make money. A well-executed trending strategy should be able to achieve this goal with ease.
A trend is a lagging indicator because it tells you that the market has been in a trend for the past period. This knowledge also allows predictions of what will happen next, but the main indication of a trend is based on past price movements.
Trends are also the most important lagging indicator. Most other lagging indicators lose their predictive power when the market is not trending, so trend analysis should be done before using other technical indicators.
Example 2: Moving Average
Another common example of a lagging indicator is a moving average. A moving average calculates the average price for the last period and plots it on the chart. Then repeat the process for all previous time periods and connect the points to a line.
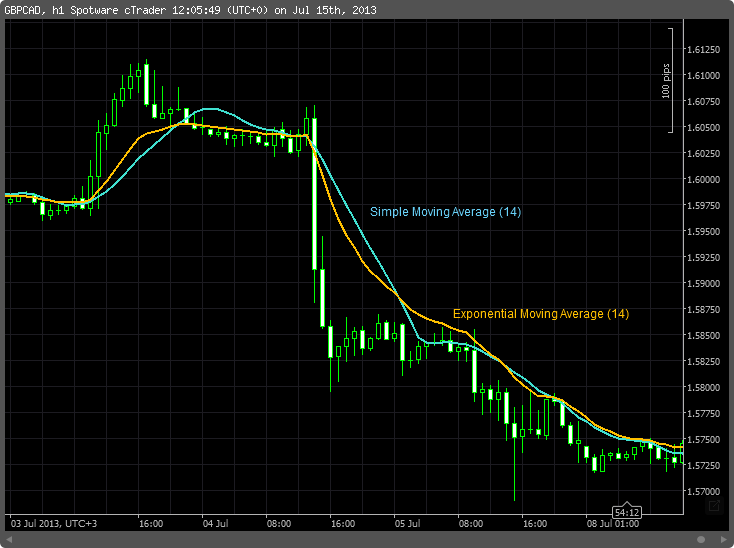
The location and direction of a moving average can tell you a lot about what an asset’s price has been doing.
- If the moving average moves up, the market must have risen during the last period. Heading downwards, the market would have declined.
- When the market trades above the moving average, the market must have risen over the past period. If the market was trading below the moving average, the market would have declined.
If these two signs point in the same direction, you’ll have a good idea of what’s going on.
- If the market trades above the moving average and the moving average is pointing upwards, the market is likely increasing.
- If the market is trading below the moving average and points below the moving average, the market is likely falling.
This sign will help you make better investment decisions.
Example 3: Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a popular indicator because they create a price channel in which the market will stay. These price channels consist of three lines or bands.
- 20-period moving average as midline.
- The line above the center line is twice the standard deviation.
- Down line that is twice the standard deviation below the mid line.
The market never leaves the outer two lines of the Bollinger Bands. The middle line acts as weak resistance or support depending on whether the market is currently above or below it.
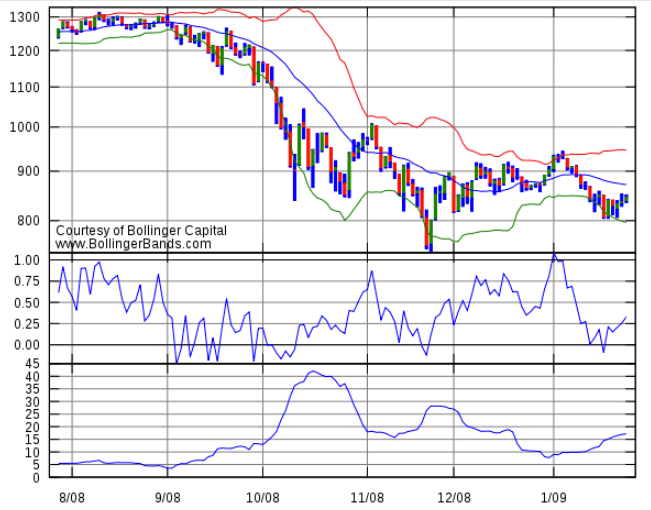
Bollinger Bands help you understand if an asset’s price will rise or fall.
- When an asset is trading near the upper range of the Bollinger Bands, it has little room to go higher. As a result, it is likely to fall.
- Once an asset is trading near the lower range of the Bollinger Bands, there is little room for further decline. As a result, it is likely to rise.
- When an asset approaches the middle line, it is likely to break. Sometimes the market may break through the middle line. Sometimes it turns around.
This sign offers many trading opportunities.
Bollinger Bands are lagging indicators because they only tell you what happened in the past. Both the moving average and standard deviation are based on the last 20 periods. While the market is likely to follow a similar forfeiture over the current period, Bollinger Bands cannot predict a trading range 50 periods from now. Then the market environment changes and the trading scope changes.
Despite these limitations, Bollinger Bands can be an important part of your trading strategy. We’ll see how later.
Why use a Lag Indicator?
Some people new to binary options question whether a lag indicator can be helpful. They claim that every trader has to predict what will happen next, and indicators that tell us what has already happened are of little help in this task.
These traders are mistaken. Lag indicators help you make valuable predictions and gain deep insight into the market. There are two main reasons traders use lagging indicators:
- The Lag Indicator is based on proven facts. There are no leading indicators.
- Understanding what happened will help you predict what will happen next.
Let’s take a closer look at the three advantages of lagging indicators.
Advantage 1: Lag indicators are based on proven facts, leading indicators are not.
When the 50 line breaks above the average, you know that asset prices have risen more than they have fallen over the past 50 years. These results are not in dispute. Likewise, if the market is currently trading below its moving average, you know that the market has picked up some downward momentum recently.
This knowledge solidifies your trading strategy. Conservative traders in particular will like the lag indicator because it gives them a certain basis on which to make decisions.
Leading indicators are different. For example, volume is a leading indicator. A volume strategy indicates the end of a movement where volume reduction is imminent. This might be true, but I’m not sure, and I can’t prove this connection. Volumes are slowing down, but the price movement itself may be accelerating. Sometimes, the volume is reduced to indicate the movement of the ending. Sometimes it isn’t.
Simply put, lagging indicators focus on past price movements. Leading indicators mean that another factor may influence future price movements. There may or may not be a connection, but since there are so many other factors that affect the market, it is impossible to say whether this connection will affect the market or whether it will have a stronger impact on the market than any other connection at all.
Benefit 2: Understanding what happened will help you predict what will happen next.
Lag indicators also allow for predictions of what will happen next. It does so indirectly.
Leading indicators mean that certain factors determine where the market will go next. The lag indicator makes no such assumption. They simply predict that what happened before will continue.
When a market breaks above a moving average, the lagging indicator only tells you what happened. The market has recently changed direction. The implied assumption is that this move will continue.
- If the market has declined over the last period, the same factors that have forced the market in the recent past are likely to decline soon as well.
- If the market has risen during the last period, the same factors that have driven the market up in the recent past are likely to rise soon.
Both predictions are tradable.
Binary options trading in general requires an understanding of what is going on. It’s impossible to say with absolute certainty because there are so many factors currently in play. However, understanding what happened is an essential part of arriving at a tradable prediction suitable for any case where you can make money.
How to Trade Lagging Indicators
Let’s be specific. Below are three strategies on how to trade lagging indicators with binary options.
Strategy 1: Trade Swing on the Trend with One Touch Options
Each trend consists of many swings. Because each single swing combines a strong indication of direction and length of the move, it provides a great trading opportunity for one-touch options.
Any move in the direction of the major trend will lead to a move in the opposite direction and vice versa. This simple relationship makes predicting the direction of the market simple once you recognize the swings.
Now, you can simply trade this signal with a high/low option, but with a swing you can trade one-touch options.
Swings from trend to state always move to the last extreme.
- In an uptrend, the next upside move will hit at least the level of the previous high.
- In a downtrend, the next down move will reach at least the price level of the previous low.
Swings in the direction of major trends follow similarly clear rules. Markets usually reverse 1/3 or 2/3 of the previous trend in the direction of the main trend.
- Down swings in an uptrend will reverse from about 1/3 to 2/3 of the previous up swing.
- In a downtrend, the uptrend reverses from about 1/3 to 2/3 of the previous down move.
With this knowledge, you can achieve clear price targets you need to trade one touch options on. Here’s what you do.
- Wait for swing to finish
- Determine the reach and direction of your next swing.
- Make sure your broker offers one-touch options with target prices and realistic expirations within this moving range. If so, trade. If not, trade the High/Low options in the direction of the move.
At this point, it is important to mention that movements in the main direction of a trend are usually more volatile and take longer to develop. Many traders avoid canceling trades with one-touch options and use high/low options instead. Decide for yourself how to trade reversal.
Strategy 2: Trade the market crossing moving averages with high/low options
When the market moves above its moving average, it seems to change direction. You can predict that this new movement will continue and invest in higher or lower options depending on the direction of the movement.
- When the market crosses below your moving average, invest in lower options.
- Invest in higher options when the market is above the moving average.
An important aspect of this strategy is choosing the right expiry. For example, a 9-period moving average cannot predict what will happen to an asset’s price 50 periods in the future. A 50 period and a 9 period are simply too different periods.
To avoid hard-to-predict predictions based on moving averages, always keep expiration times shorter than the default time for moving averages. Ideally, you’d want to use an expiration shorter than half of the moving average.
Likewise, you should avoid using too short an expiration date. Otherwise, you could lose trades even with accurate forecasts due to short-term market fluctuations. Use an expiry of at least 1/4 of an hour, which is the basis for moving averages.
For example, if you have a price chart with a moving average based on a 20-period period and a 5-minute period, the moving average is based on a 100-minute period (20 x 5). Ideally, you would trade this moving average with expiry periods of 25-50 minutes. I could go a bit longer or shorter, but an expiration of 60 seconds would be too short and one of 4 hours would be too long.
Strategy 3: Trade Bollinger Bands with Low Risk Ladder Options
Bollinger Bands represent the trading range of the market, and ladder options allow you to predict prices outside the market range. This is a great combination.
The success of this strategy depends on choosing the right expiration date. The Bollinger Bands are a lagging indicator and you can’t predict what’s going to happen in 10 years. Until then, the market has changed and the indicator of the Bollinger Bands will change along with it.
In order for the Bollinger Bands on the chart to make valid predictions for options, the chart period must be set to a value equal to or greater than the expiry. The important thing is that options expire within this time period because Bollinger Bands only generate forecasts for this time period.
When thinking of trading options with 15-minute expiry times, you should at least use a 15-minute chart. If 10 minutes have already passed within the current time period, you should switch to the 30 minute chart so that the option expires within the current time period.
Here’s what you need to do to put this strategy into action.
- Set the duration of the charcoal to the expiration period.
- Analyze the upper and lower price ranges of the Bollinger Bands.
- Kyung LeeLook for ladder options with target prices that are out of bounds.
- We predict that the market will never be able to reach this price level.
For example, assume an asset is trading at £100. The upper Bollinger Band is at £101 and the lower band is at £99.5. The expiry and chart period is 30 minutes and no time has passed in the current period.
- If your broker is offering a ladder option with a target price of £101.5, your target price is outside the Bollinger Band range. As a result, you should invest in lower options based on this target price, which you expect the market will not be able to reach at this price level.
- If your broker offers a ladder option with a target price of £100.5, you know that the target price is within the range of the Bollinger Bands. This target price would be a bad investment based on this strategy.
Payouts are relatively small with this strategy. Since you can win the overwhelming majority of trades, you should be able to profit nonetheless.
Summary
Lag indicators are an important aspect of any market analysis strategy. They give a certain indication of what happened and allow quality predictions about what will happen next. Strategies based on trends, moving averages, and Bollinger Bands have helped many traders establish successful trading strategies.
Three Examples of Technical Indicator Strategies
Here are examples of strategies you can use to help you get started with binary options and technical indicators.
One: Extreme Trading in MFI/RSI
The Money Flow Index (MFI) and Relative Strength Index (RSI) are simple to interpret technical indicators that are based on similar ideas. Both indicators are oscillators and calculate the strength of a move by relating current momentum to past momentum. The difference is that MFI also takes volume into account while RSI only focuses on price action. Choose the indicator you like more. There is little difference in the final strategy.
Both MFI and RSI define overbought and oversold areas.
- If a trader has been buying an asset for too long, the MFI and RSI assume that the market will continue to drive the price higher due to the lack of remaining buyers. The market is overbought and a turnaround is possible.
- When a trader sells an asset for too long, the MFI and RSI assume that the market continues to drive the price down due to a lack of remaining sellers. The market is oversold and a turnaround is possible.
You can trade binary options based on this simple prediction. When the selection indicators reach extreme values, invest in the opposite direction and predict that the market will return soon. Some traders argue that it is better to invest when the market leaves an extreme area, and to invest in a reversal as indicated by the market leaving the extreme area than when the market leaves the extreme area. region). Some traders also wait a period of time before investing to see if the market remains in an extreme area.
2 : Trading Bollinger Bands

Bollinger Bands are a great technical indicator for binary options traders because they clearly indicate the price levels at which price action should be expected.
Bollinger Bands create a price channel consisting of three lines. People:
- Moving average . The middle line of the Bollinger Bands is a moving average, usually based on 20 periods.
- Above line . By adding twice the standard deviation to the moving average, the Bollinger Bands create the upper line.
- lower line . Subtracting twice the standard deviation from the moving average produces a lower Bollinger band.
The result of this process is a price channel that surrounds the current market price. Each line acts as resistance or support depending on which direction the market is approaching the line.
- When the price reaches one line from the top, it acts as a support .
- When the price reaches one line below, it acts as resistance.
Traders can trade this line in two ways.
- Trade your impending turnaround time. When the market reaches the line, there will be a turnaround, at least briefly. Traders can trade this prediction and invest in the preceding movement and the opposite movement. If you use the High/Low option, this is a short-term forecast and use expiry for the length of one period. A one-touch option is also available. In this case, use a target price equal to or greater than half the distance to the next line.
- Break through the market midline. The middle line is special because it can act as resistance or support depending on where the market is currently in relation to the line. When the market breaks through the line, the meaning of the market changes. What was resistance now becomes support, and vice versa. Traders can benefit from this important event and invest in binary options in a breakthrough way.
This simple way to make money is ideal for beginners. Experienced traders may also add other indicators to confirm the predictions of Bollinger Bands (such as moving averages).
3. Average True Range Trade (ATR)
The Average True Range (ATR) is the perfect technical indicator for boundary options traders. Boundary options are a special type of binary option because they are the only ones that do not require you to predict market direction. This type of forecasting is suitable for difficult types of traders.
A boundary option defines two target prices equidistant from the current market price. One is above the current market price and the other is below it. Two wins your options; The market must trigger the target price before the option expires. You don’t have to hold the price level, just touch one target price. A boundary option is a one-touch option with two target prices.
Boundary options allow you to avoid predicting which way the market will move. Your task is to predict whether it will move far enough to reach one of the two target prices. ATR is the perfect metric for these predictions.
ATR does one simple thing. Calculate the average range for the past market period. For example, if you are looking at a chart where the ATR has a value of 10 and a period of 10 minutes, the asset has moved an average of 10 points in each past 10 minutes.
You can adjust the number of periods for ATR to analyze. Most traders use a 14 period setup. In other words, ATR calculates the average range of the last 14 periods on the chart.
To trade boundary options based on the ATR, you only need to compare the ATR’s reading to the target price.
Let’s go back to our previous example. On a chart with a 10-minute period, ATR has a value of 10. If your broker offers a target price option that is 30 points away and expires 1 hour, there is a good chance the market will reach one of the target prices. Your reasoning is:
- The market moved 10 points per period.
- To reach the target price in a straight line movement, the market must move 5 points per period. (The expiration of the option is 60 minutes, and you are looking at a 10-minute chart. This means that the option has 6 periods until it expires. The target price is 30 points away. Divided into 6 periods, the market moves in a straight line. You need to move an average of 5 points per period to reach the market price.)
- The average movement of the market per period is twice the movement required to reach the target price.
- Normally markets never move in a straight line, but if they move in two consecutive directions in the same direction, they almost exist. Therefore, the target price is more likely to be reached.
As you can see from this example, you should always discount the maximum reach of the market. If the market has been moving in the same direction for 60 minutes, you will have a range of 60 points. This will never happen, which is why many traders use the discount factor. For example, after multiplying your maximum reach by 0.5, you invest if the target price of a boundary option is closer than the result of this equation.
You can choose a discount factor based on your risk tolerance and experience. A factor of 0.5 or less is recommended. Higher factors are too risky.
Also consider the payout for your options. Some brokers offer high risk boundary options (far target price, high payout) and low risk boundary options (high target price, low payout). Higher payouts allow you to trade profitably when you win fewer trades, allowing you to take more risk and use higher discount rates.
Some traders also use the Average Directional Movement Index (ADX). ADX represents trend strength on a scale of 0 to 100. 0 indicates complete absence of direction. 100 means all cycles point in the same direction. You can calculate the discount factor by dividing the value of ADX by 100.
- If ADX reads 40, use a discount rate of 0.4
- A ADX of 70 uses a reading factor of 0.7
This strategy allows you to tailor your discount factor to the current market environment.
A final word on technical indicators
Technical indicators and binary options are a great combination. Technical indicators allow you to make short-term forecasts in any market. Binary options allow you to trade these predictions more profitably than other types of trades.
There is an indicator for every strategy like examples of MFI/RSI, Bollinger bands or ATR shows. Find the indicator that’s right for you. You have taken a big step towards becoming a successful trader.
If you still need a broker that allows you to trade binary options, take a look at our list of the best brokers.